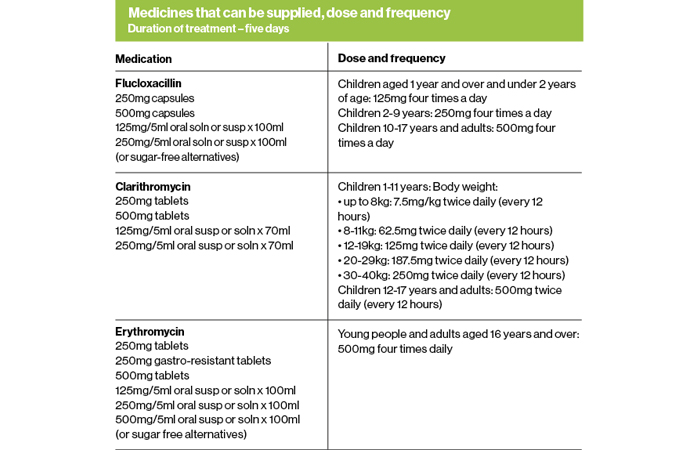
Using the infected insect bites and stings PGDs
For patients who pass the Gateway Point and are likely to have an infected bite or sting, there are three antibiotic options for treatment:
1. Flucloxacillin – for children aged 1 year and over and adults
2. Clarithromycin – for children aged 1 year and over and adults, where flucloxacillin is not appropriate due to hypersensitivity
3. Erythromycin – for young people and adults aged 16 years and over who are pregnant, or where pregnancy is suspected and where flucloxacillin is not appropriate due to hypersensitivity.
Confirm the patient meets the criteria for inclusion, but before offering flucloxacillin as first choice antibiotic, check whether the patient:
- Is systematically unwell
- Has a known co-morbidity which may complicate or delay resolution of the infection (e.g. peripheral arterial disease, chronic venous insufficiency, lymphoedema, morbid obesity)
- Has severe pain out of proportion to the wound
- Has a significant collection of fluid or pus at the site of infection.
If any of these conditions are present, the patient should be referred to their GP. Then determine whether there are other reasons why the patient might be excluded from treatment.
General criteria for exclusion include:
- Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy in individuals under 16 years of age
- Individuals who are immunosuppressed or are currently taking immunosuppressants (including systemic corticosteroids) or immune modulators
- Severely immunosuppressed individuals (as defined in Chapter 28a of the Green Book – see panel)
- Known hypersensitivity to the antibiotic
- Failed previous antibiotic for this episode of infected insect bite or sting
- Individuals following a ketogenic diet
- Any individual suspected of having a systemic reaction to an insect bite or sting, i.e. angio-oedema or anaphylaxis
- Previous systemic allergic reaction to the same type of bite or sting
- Previous or current known methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonisation or infection
- Previous or current history of liver disease
- Known chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 5 (eGFR <15ml/min/1.73m2)
- Less than 3 days before receiving, or within 3 days after receiving, oral typhoid vaccine
- Concurrent use of any interacting medicine.
Refer to the PGDs for a specific list of exclusions for:
- Flucloxacillin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin.
In addition to medication, each patient treated under a PGD should:
- Be given the appropriate medicine patient information leaflet
- Provided with self-care advice
- Provided with TARGET self-care leaflet
- Given information on insect bites and stings e.g. from the NHS website
- Where relevant, patients should be provided with information from: UKHSA: Tick awareness and The Anaphylaxis Campaign: INsect sting allergy - the facts.
Definition of severe immunosuppression
Individuals with primary or acquired immunodeficiency states due to conditions including:
- Acute and chronic leukaemias, and clinically aggressive lymphomas (including Hodgkin’s lymphoma) who are less than 12 months since achieving cure
- Individuals under follow-up for chronic lymphoproliferative disorders including haematological malignancies such as indolent lymphoma, chronic lymphoid leukaemia, myeloma, and other plasma cell dyscrasias
- Immunosuppression due to HIV/AIDS with a current CD4 count of below 200 cells/mcl
- Primary or acquired cellular and combined immune deficiencies – those with lymphopaenia or with a functional lymphocyte disorder
- Those who have received an allogeneic (cells from a donor) or an autologous (using their own cells) stem cell transplant in the previous 24 months Those who have received a stem cell transplant more than
24 months previously but have ongoing immunosuppression or graft versus host disease (GVHD).
Individuals on immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapy including:
- Those who are receiving or have received in the past 6 months immunosuppressive chemotherapy or radiotherapy for any indication
- Those who are receiving or have received in the previous 6 months immunosuppressive therapy for a solid organ transplant
- Those who are receiving or have received in the previous 3 months targeted therapy for autoimmune disease, such as JAK inhibitors or biologic immune modulators including B-cell targeted therapies, monoclonal tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), T-cell co-stimulation modulators, soluble TNF receptors, interleukin (IL)-6 receptor inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitors.
Individuals with chronic immune mediated inflammatory disease who are receiving or have received immuno-suppressive therapy
- Moderate to high dose corticosteroids (equivalent ≥20mg prednisolone per day) for more than 10 days in the previous month
- Long-term moderate dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≥10mg prednisolone per day for more than 4 weeks) in the previous 3 months
- Any non-biological oral immune modulating drugs e.g. methotrexate >20mg per week; azothioprine >3.0mg/kg/day; 6-mercaptopurine >1.5mg/kg/day, mycophenolate >1g/day) in the previous 3 months
- Certain combination therapies at individual doses lower than stated above, including those on ≥7.5mg prednisolone per day in combination with other immunosuppressants (other than hydroxychloroquine or sulfasalazine) and those receiving methotrexate (any dose) with leflunomide in the previous 3 months.
Individuals who have received a short course of high dose steroids (equivalent >40mg prednisolone per day for more than a week) for any reason in the previous month.