Key information from the patient history
Age: Acute sinusitis can affect any age group but is less common in children because their sinuses are not fully developed. The Pharmacy First service in England is aimed at adults and children aged 12 years and over. Pregnant teenagers under 16 years of age should be referred.
Duration: Most cases of sinusitis will improve by day 10 and resolve in two to three weeks. Chronic sinusitis is defined as symptoms lasting for more than 12 weeks. Symptoms for around 10 days or less are more likely to be associated with a preceding cold rather than viral or bacterial acute sinusitis.
Associated symptoms:
- The affected sinus often feels tender when pressure is applied. It is typically worse on bending forwards or lying down
- The pain may be felt behind and around the eye, or over the cheek, with radiation over the forehead. Often only one side is affected
- The headache may be associated with runny nose or nasal congestion
- Fever (above 38˚C).
Previous history: Ask whether there has been a marked deterioration in symptoms following a recent cold that had started to settle (so called ‘double sickening’) as this may be an indication of bacterial infection.
Patients may have had episodes of acute sinusitis previously. Recurrent episodes may relate to an incomplete response to an antibiotic (sometimes due to resistance, or anatomical abnormalities affecting drainage, or nasal polyps). Patients who have had acute sinusitis before may have the expectation that they will receive antibiotics if this has happened in the past.
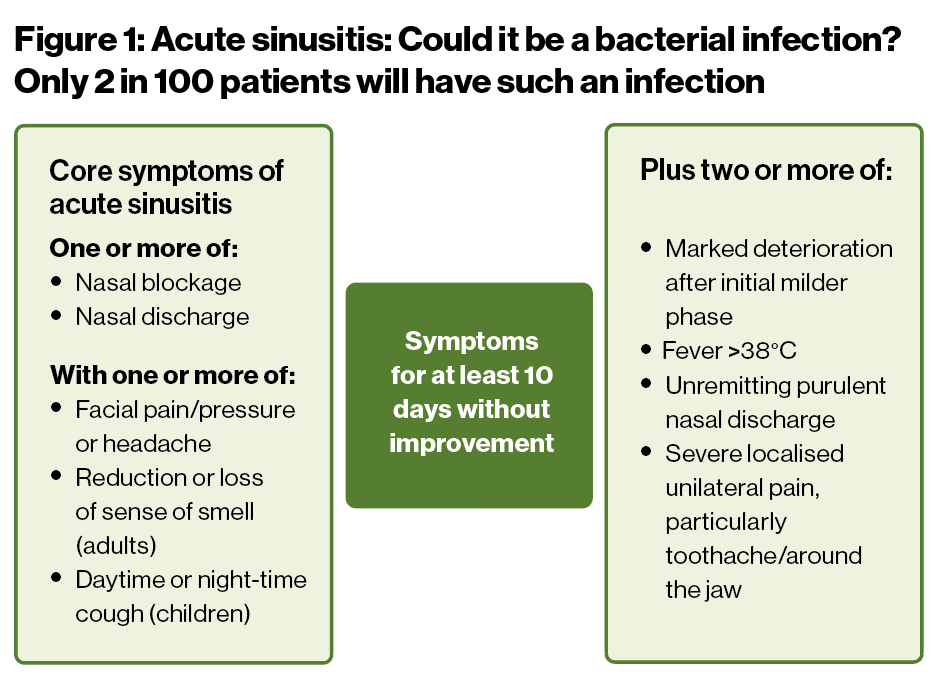
The features of a bacterial infection are summarised in Figure 1 below.